Tomayto or Tomahto?
While Open Banking, Open Finance, and Embedded Finance may all seem like buzz words commonly heard in the financial industry, the concepts themselves create vast opportunities for financial innovation. And yes, they do actually have different definitions and meanings. Often eliciting confusion, this blog post breaks down what each concept really means for you and how they can offer you better financial experiences.
So… What's Open Banking?
No, it doesn’t just mean the bank is now open (although it kind of does…) — Open Banking is an emerging practice granting financial institutions the ability to share consumer-permissioned data with third parties, like FinTechs. Through Open Banking, banking data that would otherwise be stuck with your bank can be shared with other financial providers - essentially, it enables the secure exchange of your banking data. With open banking, bi-directional connectivity (meaning info to your bank and info from your bank) between financial institutions and trusted third parties has been enabled. Authorized data can be used from, shared with, and sent to the bank.
How Europe’s PSD2 Regulation is Driving Open Banking
A key catalyst contributing to the adoption of Open Banking arises from the European regulation, Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2). PSD2 is largely seen as the ‘starting point’ of Open Banking. The PSD2 regulation requires financial institutions (FIs) to make customer data available to third party financial services providers (like FinTechs!). While PSD2 did not invent Open Banking, it has accelerated its adoption and enabled transformative change in Europe’s financial services industry.
Digital adoption is estimated to have accelerated as much as five years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, as businesses shifted to digital processes in order to interact with customers and suppliers, collaborate with partners and vendors, and in some instances, in order to just reopen and operate their business.
Customer expectations also evolved alongside this shift, as customers now expect more digital and intuitive experiences — including in the banking sector. By sharing data through APIs with third parties, typically through FinTechs, more innovative and streamlined customer experiences are possible. While data sharing may seem daunting, consumers actually gain more control and increased opportunities — when data is available outside of your financial institution, you have the option to access other financial services while still being with your original bank. Snoop, a money management app, aggregates consumer’s authorized financial data to identify cost-saving opportunities, such as ways to save on household bills. By electing to share their banking account data with Snoop, consumers gain greater visibility into their financial wellbeing and more control over their budgeting.
APIs: The Key to Open Banking
The secure exchange of data as outlined by Open Banking is all made possible from Financial Application Programming Interfaces (Financial APIs). Financial APIs are a software application which use a set of protocols and codes to enable communication between application software. Coined the bridge between financial institutions and FinTechs, APIs act as intermediaries by processing and relaying information requests. In other words, consider APIs as the proverbial plumbing which enables digital experiences. In using APIs, financial institutions can seamlessly connect their platforms to various products and services.
Moving Beyond Open Banking
As mentioned above, PSD2 is seen as the regulatory ‘starting point’ of Open Banking. While it benefits customers, it is not the ‘be-all and end-all’ of Open Banking. What’s more, not all functionalities are covered by the European regulation, especially as operational complexities increase within the commercial banking space. As more and more financial institutions adopt Open Banking practices, it’s crucial that they continue to innovate in order to stay ahead and stand out from the competition.
So… What's Open Finance?
Open Finance branches upon Open Banking and presents opportunities for a broader category of capabilities. As can be inferred by the name, Open Banking relates more specifically to banking capabilities, whereas Open Finance relates to an individual’s broader financial footprint and is more of a framework for how open banking should function. Accenture describes Open Finance as “a data sharing model where customers can agree to share the data from any transaction that involves the exchange of money”.
MX is a FinTech leveraging Open Finance to create better user experiences. In creating Open Finance APIs, MX enables banks and other FinTechs to make better use of their financial data, whether it be connecting accounts, or gaining insights through their data. Extending past Open Banking, MX offers solutions to customers in Financial Wellness, Digital Banking, Payments, Lending, and Crypto. As explained by MX, “in Open Finance, consumers grant trusted third parties access to their financial footprint for better experiences and personalized solutions to improve financial wellness.”
Personal Financial Management (PFM) digital solutions enable consumers to manage their financial footprint and gain greater visibility into their financial wellbeing. PFM platforms like Strands analyze consumer financial behavior and identify spending patterns to provide personalized insights. With real-time visibility into their financial position, consumers can better manage and understand their financial wellness.
So… What's Embedded Finance?
All this leads us to Embedded Finance. Going a step above the capabilities offered by Open Banking and Open Finance, Embedded Finance is the act of integrating banking capabilities into non-financial services. Through technology, financial platforms are embedded within non-financial services. It’s all about leveraging the capabilities and protocols enabled by Open Banking and using them to embed services into the customer journey. Embedded finance enables opportunities for innovation within multiple touchpoints of the customer journey, leading to enhanced user experiences. The practice eliminates pain points by streamlining banking capabilities into consumers’ everyday processes.
In Practice - The State Before Embedded Finance
Financial professionals spend the majority of their time in the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or accounting systems. ERP and accounting systems are home to core operational processes: from distribution, financials, CRM… just about everything. What is missing from this list, however, is one core operation: banking. Now, if a financial professional needs to perform their treasury management services, they’ll have to embark in the infamous practice of ‘swivel chair’ accounting: manually inputting data into one screen, turning to the other (or, second, or third…) monitor and inputting that same data over, and over (and over) again. This manual process presents opportunities for error, is time consuming, and, frankly, deflects from strategic tasks.
The New Opportunity - FISPAN’s Embedded Banking Experience
Embedded finance is the space that FISPAN operates in. Beyond simply exchanging data, FISPAN embeds banking capabilities into commercial clients’ ERP and accounting systems. The result? Financial professionals are able to perform their treasury management services in the place they do business: their ERP.
Rather than navigating between their banking portal and ERP or accounting systems, banking functions are accessible in one central location. Leveraging the ability to securely exchange data with financial institutions as outlined by Open Banking, FISPAN uses a two-way connection set up with the bank. Through APIs, the necessary customer data is transformed and translated into commercial banking clients’ ERP systems. Now, customers have access to the banking capabilities they need, when they need them.
So… Here’s the Difference 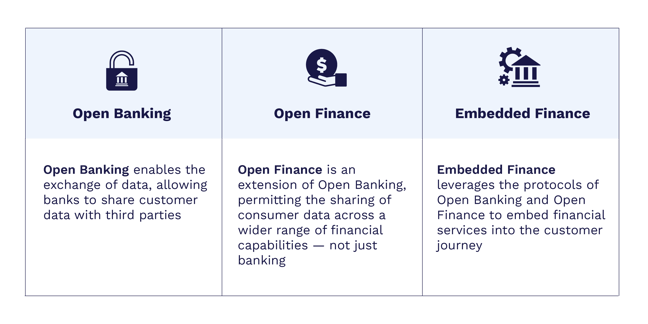
Contact us to see how you can take advantage of FISPAN’s Embedded Banking solution in the place you already do business: your ERP.



