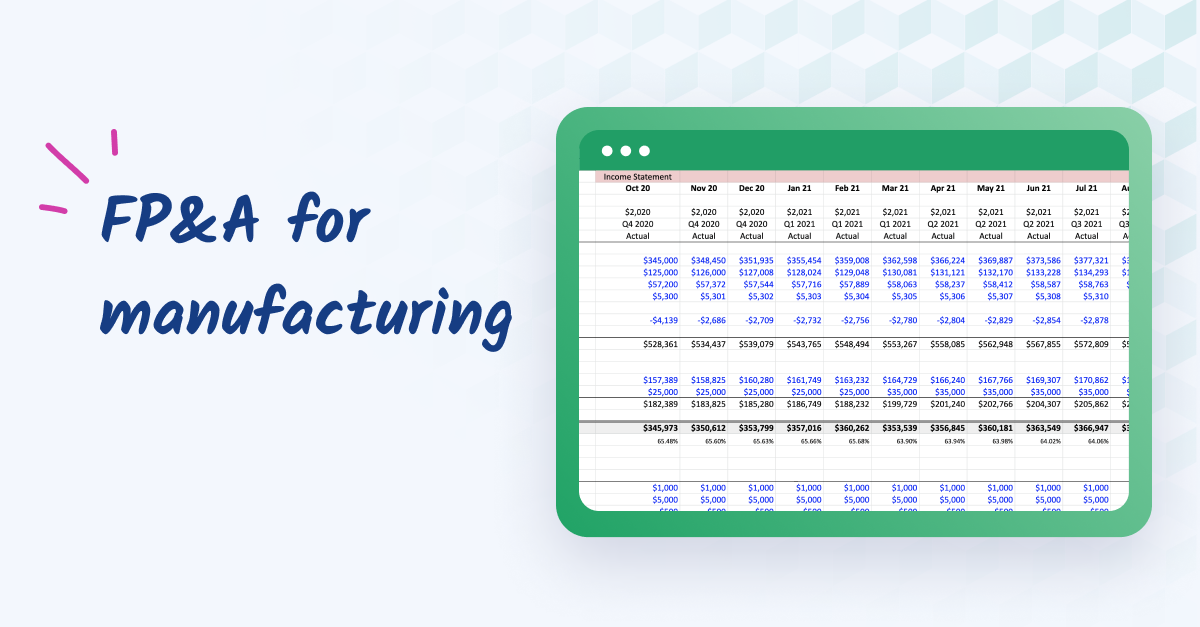
Understanding the manufacturing industry from an FP&A perspective
The manufacturing sector encompasses a variety of production environments, each impacting financial planning in distinct ways.
In job-based manufacturing, products are made to order, which requires precise budgeting for specific projects. Batch production involves producing large quantities of the same item, necessitating efficient management of inventory costs and production schedules. Continuous production, operating non-stop, demands relentless attention to operational costs and efficiency.
Financially, the manufacturing industry is marked by significant investments in machinery and technology, sensitivity to economic cycles that affect demand, and long periods required to develop and produce products. These factors make careful planning essential to ensure that resources are used effectively and that the company can adapt to changes in demand without jeopardizing its financial health.
For FP&A professionals in manufacturing, understanding these environments and characteristics is essential. This knowledge allows them to tailor financial strategies that not only tackle immediate financial needs but also align with broader business objectives, ensuring sustained operational success.
Core components of effective FP&A in manufacturing
Effective FP&A in manufacturing hinges on four key components that ensure the financial health and strategic alignment of the business.
Budgeting
Accurate budgeting is fundamental in manufacturing due to its cyclical production schedules and significant capital expenditures. To manage this, FP&A professionals must employ techniques that accommodate the timing of cash flows, plan for large purchases of equipment, and allocate funds for upcoming production cycles. This might involve setting aside reserves during peak production periods to cover slower times or unexpected expenses.
Forecasting
In a sector known for market volatility, having reliable forecasting tools is essential. FP&A teams should use a combination of historical data and market trends to predict future conditions. Implementing rolling forecasts can also provide flexibility, allowing the company to adjust its financial strategy as new information becomes available and market conditions evolve.
Reporting
Effective reporting in manufacturing FP&A should focus on clarity and relevance, providing stakeholders with insights that are directly actionable and support strategic decision-making. Reports should highlight key financial metrics and trends, outline potential risks, and measure progress against strategic goals. Regular updates are crucial to keep everyone informed and prepared to act quickly when necessary.
Variance analysis
This is a critical tool for tracking actual financial performance against the budgeted figures. By regularly conducting variance analysis, FP&A professionals can identify where the business is deviating from its financial plan, understand why these deviations are occurring, and adjust operations accordingly. This process helps in fine-tuning budgeting and forecasting models over time, ensuring they remain accurate and effective.
By mastering these components, FP&A leaders in manufacturing can ensure their financial strategies are not only reactive to immediate needs but also proactive in fostering long-term growth and stability.
FP&A in manufacturing: leveraging the right technology
In manufacturing FP&A, leveraging technology is not just about keeping up with trends—it’s about gaining a strategic edge through improved accuracy, efficiency, and foresight in financial planning.
ERP systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are crucial for streamlining financial data gathering in manufacturing. These systems integrate all facets of an operation, including inventory, procurement, production, and finance, providing a holistic view of the company’s financial health. This integration helps FP&A professionals quickly access accurate data, reducing the time spent on compiling information from disparate sources and increasing the time available for analysis and strategic decision-making.
FP&A software
Manufacturing-specific FP&A software offers tools tailored to the unique needs of the industry. These tools can handle the complexities of manufacturing finance, such as managing the costs of raw materials, production processes, and distribution. Specialized software provides more nuanced insights into cost behaviors and profitability, enabling more precise budgeting and more strategic resource allocation.
Advanced analytics and AI
The use of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) in manufacturing FP&A can significantly enhance the accuracy of forecasts and the effectiveness of scenario planning. AI algorithms can process large volumes of data to identify patterns that might not be evident through traditional analysis. This capability allows for more accurate predictions of market demand, supply chain disruptions, or production bottlenecks. Additionally, scenario planning can be enriched with AI by simulating various market conditions and their potential impacts on financial performance, helping leaders make informed, data-driven decisions.
By embracing these technological tools, FP&A teams in manufacturing can not only streamline their operations but also anticipate future challenges and opportunities, leading to better-prepared, more competitive businesses.
Best practices for strategic decision-making in manufacturing
Strategic decision-making in manufacturing FP&A requires a comprehensive approach that aligns financial activities with overarching business objectives. Here’s how FP&A professionals can navigate this critical aspect:
- Linking financial plans with corporate strategy: The alignment of financial planning with long-term corporate strategies ensures that every financial decision supports broader business goals. This means setting financial targets that reflect the company's strategic priorities, such as market expansion, sustainability initiatives, or product innovation, and ensuring that resources are allocated accordingly to achieve these objectives.
- Capital allocation strategies: Effective management of investments in equipment and technology is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the manufacturing sector. FP&A teams must evaluate the potential returns of such investments against their costs, considering both short-term impacts and long-term benefits. This involves not just purchasing decisions but also decisions about when to upgrade existing equipment or invest in new technologies that could drive efficiency and productivity.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks is vital to safeguard the company’s assets and future profitability. This includes managing risks related to currency fluctuations, changes in commodity prices, and disruptions in supply chains. FP&A professionals use financial modeling and scenario analysis to predict and prepare for these risks, ensuring the company can react swiftly and effectively.
- Cost control and optimization: Maintaining control over costs is essential in manufacturing, where margins can be tight. FP&A plays a role in identifying areas where costs can be reduced without compromising quality. This might involve finding more cost-effective raw material sources, improving energy efficiency, or optimizing labor costs through better scheduling and training.
- Performance monitoring: Regular monitoring of financial performance against benchmarks and forecasts allows for continuous improvement. This includes tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like production costs, profit margins, and ROI. By keeping a close eye on these metrics, FP&A teams can quickly spot trends, make adjustments, and inform leadership about necessary strategic shifts.
- Cash flow management: Effective cash flow management ensures that the business remains solvent and can fund its operations and growth. This involves careful timing of accounts receivable and payable, maintaining adequate cash reserves, and forecasting cash flow needs based on production cycles and investment plans.
By focusing on these areas, FP&A leaders in manufacturing can make strategic decisions that not only address current financial needs but also position the company for future success. This proactive approach in aligning financial tactics with strategic goals is essential for thriving in the competitive manufacturing landscape.
Conclusion: mastering FP&A for manufacturing
Mastering FP&A is key to success in the manufacturing industry. By focusing on practical budgeting, reliable forecasting, clear reporting, and detailed variance analysis, FP&A professionals can make smarter decisions that boost the company's financial health.
Want to learn how Cube can help you on this journey? Request a free demo today.


.png)